🗣️ Artikel ini juga tersedia dalam Bahasa Melayu: Klik di sini untuk membaca versi Bahasa Melayu
Introduction
Accounting is often called the “language of business” — and for a good reason. Every decision you make as an entrepreneur, from buying supplies to pricing your products, involves money. Without accurate financial records, you’re practically flying blind. It becomes difficult to track performance, control expenses, or even stay compliant with tax laws. This article is created to help you, as a new entrepreneur, understand the basics of accounting clearly and practically, even if you have no prior background.
What Is Accounting?
In simple terms, accounting is the process of recording, organizing, and summarizing financial activities. These include everything from money coming in (revenue) to money going out (expenses), as well as what the business owns (assets) and owes (liabilities).
There are two main parts to accounting:
- Bookkeeping – the daily task of recording financial data like sales, purchases, receipts, and payments.
- Financial Reporting – analyzing those records to understand business performance and guide decision-making.
Why Is Accounting So Important for Your Business?
Many small business owners overlook accounting at first. However, understanding it is crucial if you want your business to thrive. Here’s why:
✅ Know Your Profit and Loss
Accounting helps you understand whether your business is making money or losing it. You can’t improve what you don’t measure.
✅ Manage Cash Flow
Even profitable businesses can fail due to poor cash flow. Accounting helps you monitor how money enters and leaves your business, so you can avoid shortfalls.
✅ Make Informed Business Decisions
Do you need to reduce expenses? Is it time to raise your prices? With good accounting records, you can make strategic decisions backed by data.
✅ Prepare for Tax and Audit
You’ll need accurate records to file taxes properly. If you’re audited, having organized accounts can save you from penalties and stress.
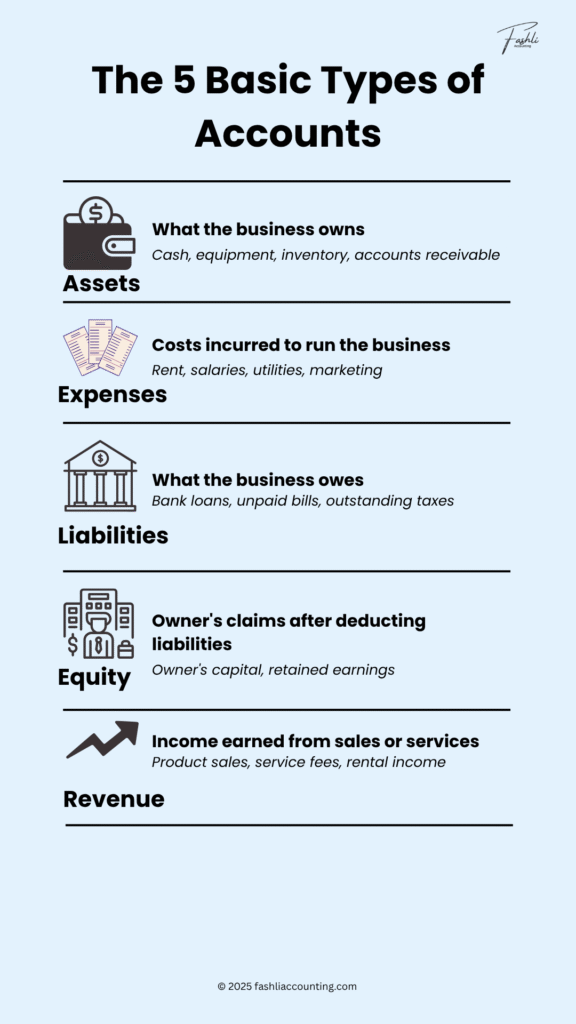
The 5 Basic Types of Accounts in Accounting
Every financial transaction in your business affects one or more of these five account categories:
| Types of Account | Explanation | Examples |
|---|---|---|
| Asset | Assets are everything the business owns that has value. | Cash, inventory, office equipment, accounts receivable |
| Expenses | These are the costs required to operate your business. | Rent, salaries, marketing costs, utility bills |
| Liabilities | Liabilities are debts or obligations that your business needs to pay. | Bank loans, unpaid supplier bills, and taxes payable. |
| Equity | Equity is the owner’s share in the business after all liabilities are paid. | Owner’s capital, retained earnings, and additional investments. |
| Revenue | Revenue refers to income generated through the sale of goods or services. | Product sales, consultation fees, and commissions. |
Example Situations (With Debit and Credit Entries)
💡 Here are simplified examples to help you understand how basic accounting entries work using the double-entry system (debit & credit): Debit & Kredit
| Situation | Debit | Credit |
|---|---|---|
| Asset: You buy a laptop for business | Equipment (Asset) ↑ | Cash (Asset) ↓ |
| Expenses: You pay a monthly rent of RM600 | Rent Expense ↑ | Cash ↓ |
| Liabilities: You take a RM10,000 loan from the bank | Cash ↑ | Bank Loan (Liability) ↑ |
| Equity: You invest RM5,000 into the business | Cash ↑ | Owner’s Capital (Equity) ↑ |
| Revenue: You provide accounting services worth RM2,000 | Cash ↑ | Service Revenue ↑ |
What Software Can You Use for Accounting?
You don’t need to do everything by hand. Today’s accounting software can make your life easier, especially if you’re managing multiple clients, products, or expenses. Some of the most widely used software includes:
- SAP ERP – powerful for larger businesses or those dealing with supply chains
- MYOB – popular in Malaysia and Australia; great for SMEs
- Yardi – used mainly in real estate and property management accounting
Most software platforms let you:
- Generate invoices
- Track income and expenses
- Reconcile bank accounts
- Run financial reports in just a few clicks
Basic Accounting Principles You Should Know
To ensure your records are accurate, there are a few basic accounting principles that guide how financial information should be recorded and presented:
- Consistency
Once you choose a method for recording transactions (e.g., cash or accrual basis), stick with it unless there’s a valid reason to change. - Reliability
Only record transactions that have verifiable and valid documentation — receipts, contracts, or bank statements. - Matching Principle
Expenses should be recorded in the same period as the revenues they help generate. This gives a clearer picture of business performance. - Accrual Principle
Record income when earned and expenses when incurred — not only when cash changes hands. - Going Concern
Assume that the business will continue operating unless there’s clear evidence otherwise.
By following these principles, your financial data becomes more trustworthy and usable for analysis or decision-making.
Common Accounting Mistakes Made by Small Business Owners
New entrepreneurs often make small accounting mistakes that can lead to bigger problems down the road. Here are some of the most common:
❌ Mixing Personal and Business Finances
Always separate your personal and business bank accounts. It makes tracking and reporting easier.
❌ Not Keeping Receipts
Without documentation, you might miss out on valid deductions or fail to prove your expenses during audits.
❌ Delaying Data Entry
Putting off bookkeeping leads to confusion, errors, or missed payments. Try to update records weekly or use software with automation features.
❌ Ignoring Tax Deadlines
Late filing or payments can cause penalties. Use reminders or consult a tax agent to stay compliant.
❌ Not Reviewing Reports Regularly
Your income statement, balance sheet, and cash flow reports help you monitor growth, spot risks, and plan better.
Avoiding these mistakes will save you time, money, and stress.
How to Learn Basic Accounting Practically
You don’t need to be a certified accountant to understand accounting fundamentals. Here are some practical ways to learn:
📚 Online Courses
Free platforms like YouTube, Coursera, and Udemy offer beginner-friendly courses on bookkeeping and accounting.
💻 Try Accounting Software
Hands-on learning is best. Use trial versions of software like MYOB, Wave, or QuickBooks to simulate recording transactions.
🧾 Practice with Real-Life Examples
Start by recording your own business expenses and income using Excel or an app. Apply what you learn immediately.
📝 Join Forums or Communities
Entrepreneur groups, accounting forums, or even Reddit can help answer your questions and guide you when you’re stuck.
📖 Read Simple Accounting Blogs
You can also learn by reading blog articles written in plain language for small business owners.
One example is fashliaccounting.com — a bilingual blog that offers easy-to-understand accounting guides, tips on using software like MYOB and SAP, and practical examples tailored for Malaysian entrepreneurs.
Learning a little each week can give you a strong financial foundation without formal schooling.
Conclusion
Accounting doesn’t have to be difficult or intimidating. By learning the basic principles and using tools designed for small businesses, you can manage your money like a pro — even without a financial background.
In upcoming articles, we’ll walk you through how to record your first transaction, set up your chart of accounts, and get started using real accounting software like MYOB or SAP.
🗣️ This article is also available in Malay: Baca versi Bahasa Melayu
